Small cells are low-power cellular radio access nodes that operate in licensed and unlicensed spectrum and provide a lower coverage range than macrocells.
Small cells which are base stations should not be confused with customer premise equipment (CPE) such as LTE or NR routers that provide Internet access to homes and businesses.
See the example below for small-cell CBRS Devices (class A CBSDs) used in SAS/CBRS private LTE network deployments.
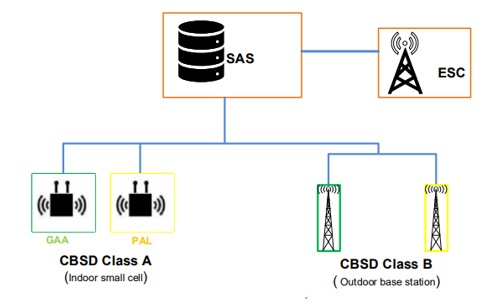
Indoor small cells for CBRS network architecture. Learn More about CBRS
For faster and easier deployments, small cells can utilize wireless backhaul technologies like PtP Microwave links or 3GPP IABs (Integrated Access and Backhaul).
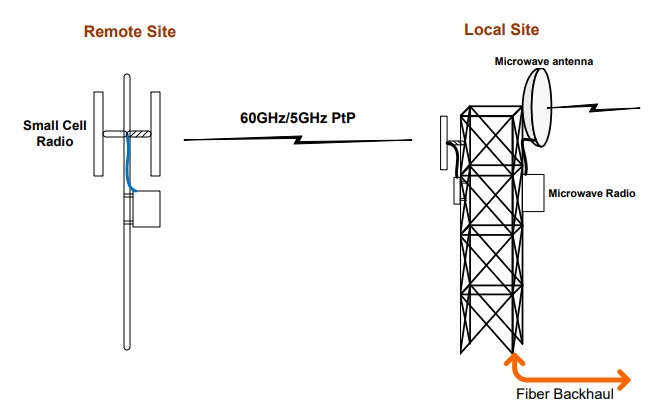
Example of microwave small cell backhaul. Learn more about PtP Link.
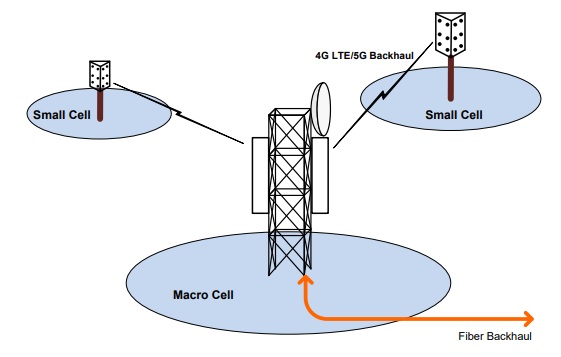
Example of IAB small cell backhaul
Small are particularly important for 5G coverage at millimeter-wave (mmWave) frequencies because of the shorter range of mmWave that requires much denser cells to cover the same area. The solution also allows the re-use of frequencies.
Powering Small cells
Small cells and other wireless backhaul equipment can be powered directly from streetlights or other outdoor luminaires that include photocell control. Power taps are required to tap power from the streetlight without interfering with photocell operation.
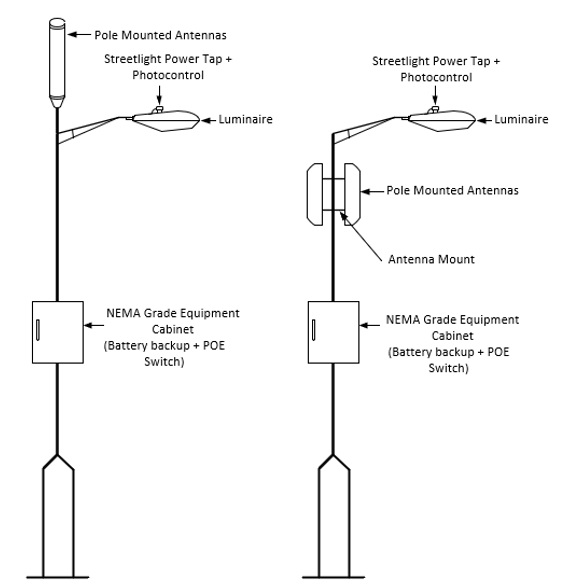
Example streetlight mounted small cells powered via photocell power tap adapters. Learn more.
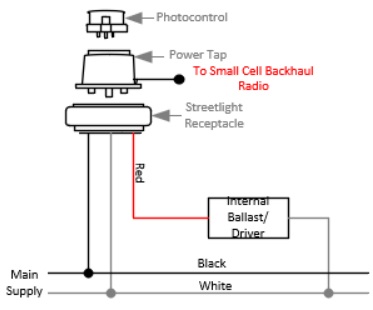
Example 3-pin photocell power tap adapter to power small cell and backhaul radio. Learn more.
For backup power, off-grid solar modules and outdoor uninterruptible power suppliers (outdoor UPS) can be used.
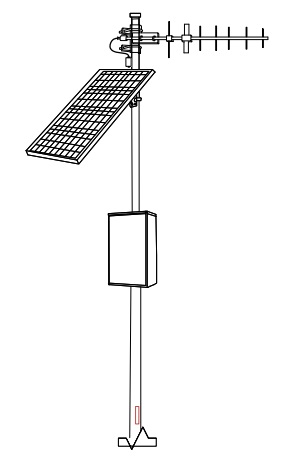
Small Cell and Backhaul Radio
Small cell infrastructure
Small cell networks can be deployed on top or on the side of buildings. They can use power from buildings with battery back-up and charging system and with appropriate mounts.

Indoor small cells can be mounted on a ceiling, wall, or placed on a desktop (like Verizon's network extender) to create indoor or stadium cellular coverage. This is ideal in areas where indoor signal penetration is poor.
Traditional categories of small cells
Femtocells: a small, low-power cellular base station, typically designed for use in a home or small business
Picocells: A picocell is a small cellular base station (BS) that is an alternative to a repeater or distributed antenna system. Spans about (98 to 328 feet) 30 to 100 meters
Microcells: A microcell is a cell in a mobile phone network served by a low-power cellular base station (tower). Covers a limited area such as a mall, a hotel, or a transportation hub.
The FCC has recently provided a framework relevant to small wireless facilities deployment more.
View Small Cell Devices supported in RFWEL's Wireless Device Information website: 
Please contact an RFWEL indoor-coverage specialist for design, infrastructure selection, and installation of small cell networks.


