TV whitespace (TVWS) refers to the unused TV channels in a range of active ("in-use") TV channels. These white spaces came about after the repacking of analog TV channels into Digital. Most countries, including the United States, have opted to use TVWS to provide broadband internet access while coexisting with the active TV channels.
In the US, the TVWS spectrum covers the 54-698 MHz bands. In 2010, the FCC made this underutilized spectrum available for unlicensed public use. With the use of a database manager and whitespace devices (WSD), these channels can be used for broadband Internet connectivity.
The database manager is used to check channel availability and communicate back to the master WSD information regarding which channel and power level to operate on among other parameters.
View Regulation: 47 CFR Part 15, Subpart H - White Space Devices
Advantages of TVWS over Wi-Fi
- Provides a wider coverage than traditional Wi-Fi, over 10Km. Lower frequencies provide larger coverage because free space path loss is proportional to the square of the frequency hence lower frequency means lower signal losses hence wide coverage.
- Perform better in non-line-of-signt (NLOS) situations due to the ability of the lower frequency band (UHF band) to penetrate obstacles such as trees, buildings, and uneven terrain.
- Better coverage means deployments can get away with less transmitters which lower infrastructure costs.
- There is more free available spectrum compared to traditional Wi-Fi (particularly interference-free spectrum), especially in the rural markets.
- TVWS broadband is easy to deploy and maintain due to the ease of spectrum management unlike traditional Wi-Fi which uses unlicensed 2.4 and 5Ghz, where it can be difficult to accurately predict channel availability at different times.
Disadvantages of TVWS
- Lower frequency operation typically means larger antennas (antenna size generally proportional to the wavelength, i.e., inversely proportional to the frequency). Larger antennas make it difficult to use MIMO diversity and coding gain to increase spectral efficiency. Because the total bandwidth available is also generally lower, it is difficult to achieve the theoretical speeds of competing technologies such as Wi-Fi and LTE.
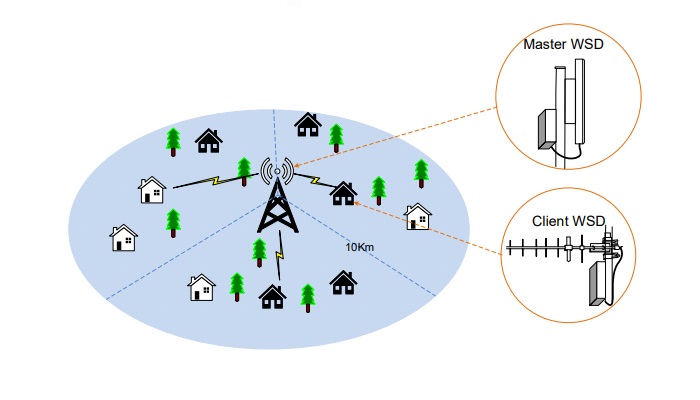
TVWS deployment involves Master WDS devices which act as the base station for the client devices and communicate to the database manager. The master WSD can use sector antennas for better coverage. The client devices connect to the BS with a directional antenna as below.
There are various applications of TVWS. These include.
- Rural Broadband Internet Access, e.g., providing VoIP for homes and businesses
- WLAN (Wi-Fi) hotspot backhaul
- Internet of Things (IoT) monitoring
- Point to Point (PtP) Backhaul
- IoT (M2M) and SCADA communications
Progress of TVWS in the U.S.
In the United States, proprietary TVWS products are available and are being used for FWA deployments. See examples of TVWS devices available.
WhiteFi
The 802.11 family includes 802.11 a/b/g/n/ac/ax and af. The IEEE 802.11af Wi-Fi Standard also known as WhiteFi is capable of using the radio spectrum within the television bands. Other upcoming standards include 802.11ba (Wake-up Radio- WUR), 802.11bb (Li-Fi), and 802.11ay (BWA via mmWave).
To find the right TV White Space antenna for your project see https://shop.rfwel.com/tvws/ or contact an Rfwel Fixed Wireless Specialist to learn more about how you can implement a TVWS Fixed-Wireless Access (FWA) project. You may also reach us at +1.480.218.1877 Option 2.


