Internet of Things (IoT), the connectivity/communication between devices (“things”) via the Internet is gaining momentum especially with the introduction of 5G.
Wireless IoT devices allow the “things” in Internet-of-Things to transmit and receive data wirelessly allowing them to be untethered to wiring infrastructure. Different IoT communication protocols have been developed to meet the low-power, wide-area coverage, and simple (low-cost) needs of IoT devices. These include communication protocols such as variants of Wi-Fi (HaLow), Z-Wave, Bluetooth, Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), Zigbee, LoRaWAN, and Cellular-IoT (CIoT) technologies include Narrow-Band IoT (NB-IoT) and LTE Category M (LTE-M).
| IoT Protocols | |
| Protocol | Description |
|
Wi-Fi
|
Although IoT devices can use standard 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands including WiFi-4, WiFi-5, and WiFi-6/6X (802.11 n/ac/ax), a new 802.11 protocol (IEEE 802.11ah also known as Wi-Fi HaLow) is being developed specifically for IoT applications. Wi-Fi Halow (802.11ah) operates in the Sub-1 GHz and offers a longer range of operation (~ 1 Km). Various enhancements to the 802.11 allow 802.11ah stations to utilize low power (allowing for extended battery life) and long-range (allowing for use in remote areas). |
|
Bluetooth and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)
|
Usually used for short distances and utilizes the ISM bands from 2402 -2480 MHz ISM band. Bluetooth can handle a lot of data but consumes more power compared with BLE. With BLE, they are used for low data transfer with low connections times, about a few mS, and, therefore, can run on battery power for long periods. |
|
Z-Wave |
This is a mesh network, usually used for home automation such as lighting control, security systems, thermostats, windows, and garage door openers. It operates in the 900 MHz unlicensed ISM band. |
|
ZigBee
|
This is the 802.15.4 based standard and uses the ISM bands (2.4 GHz, 900 MHz), Has ranges of up to 100 meters but this range can be increased with a mesh network of Zigbee devices comprising of ZigBee coordinator, Zigbee router, and ZigBee end devices. |
|
LoRaWAN, Sigfox, LoRa
|
These operate as LPWAN (Low power WAN). LoRaWAN is an 802.15.4g MAC-layer protocol. LoRaWAN links the signal to the application/s, so will contain the data transfer layer as well, enabling you to send the data to any device already connected to the cloud. Sigfox is an ultra-narrowband technology. LoRa uses proprietary frequency-modulated chirp which utilizes coding gain. LoRa is the signal and only contains the PHY layer protocol. They enable communication in lower power WAN connecting IoT devices via a central network server. They have industrial and home applications. In the US, these use the ISM 900 MHz band and 868 MHz in Europe. |
|
NB-IoT, LTE-M
|
These are competitors for Sigfox and Lora in the LPWAN space. LTE-M offers speeds of 1 Mbps (3GPP Release 13) to 4 Mbps (3GPP Release 14) for IoT applications. NB-IoT focuses bandwidth to a single narrow band of 180 kHz. They offer lower speeds (26 kbps -127 Kbps) than the LTE-M. |
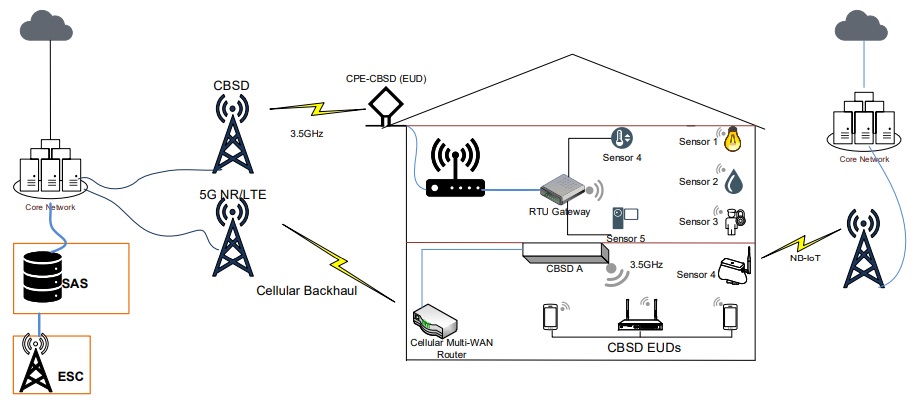
Backhauling Data from Sensors
Sensors can connect via a central RTU wirelessly or via wired connection like RS232, and Modbus. The RTU will then connect to the internet via FWA (e.g CBRS, TVWS), PtPs (e.g WiGig, Wi-Fi), Cellular, and DSL.
LTE-M and NB-IOT sensors have inbuilt modems for cellular connectivity. With the arrival of 5G, mMTC (massive Machine Type Communication, 3Gpp release 16) has also been developed. It aims to ensure connectivity of many devices including sensors, with its latency-tolerant design, and other LPWA requirements like more battery life.
Different sensors have different ranges depending on the protocol used. See the table below for comparison.
|
Protocol |
Range |
Data Rate |
Latency |
Band |
Type |
|
Wi-Fi HaLOW |
Low |
Long |
Moderate |
Sub-1 GHz |
Unlicensed |
|
Wi-Fi 5 and 6 |
Moderate |
Moderate to long |
High |
2.4 & 5 GHz |
Unlicensed |
|
LTE Cat M2 |
Low |
Moderate to long |
Moderate |
LTE/5G-NR |
Licensed |
|
LTE Cat NB2 |
Very low |
Long |
Low |
LTE/5G-NR |
Licensed |
|
LoRa |
Very low |
Long |
Low |
Low |
Unlicensed, Proprietary protocol |
|
Sigfox |
Very low |
Long |
Very low |
800 & 900 ISM |
Unlicensed, Proprietary protocol |
|
Bluetooth Low Energy |
Very low |
Short |
Low |
2.4 GHz ISM |
Unlicensed |
|
802.15 – ZigBee, Z-Wave Thread, LoWPAN |
Very low |
Short |
Low |
ISM Band |
Unlicensed |
Example of Sensors
There are water sensors that could help in avoiding or detecting flooding in buildings, control, and monitor water flow. These sensors can be placed on floors of basements, or water storages and water conduits.
Other common sensors include HVAC sensors for temperature control, camera sensors that can be connected to private databases for image scanning, motion sensors, as well as GPS sensors/receivers typically used for navigation.
With IoT, machine-to-machine (M2M) communication is important for automation and ease of monitoring and control.
Use the table below to select your SCADA or contact us for a recommendation based on your projects' needs.
| Compare Media & Protocol Converters Specs | ||
| Item | Key Specifications | Available at these Online Market Places |
|
GE D485 |
Output Interface: RS-232, RS-422, RS-485 Accessories
This product is under last time buy. Orders may be placed until 17th April 2020 and will be fulfilled based upon availability. Please contact us to discuss alternatives. |
|
|
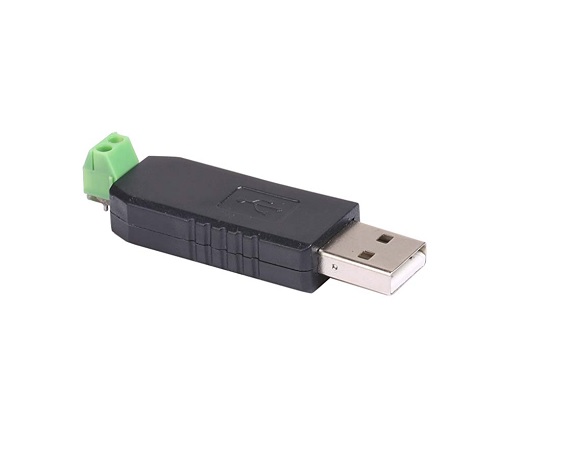
Rfwel Infra USB-RS-485 |
Input Interface: RS-485 Output Interface: USB |
|
|
GE P485 |
Input Protocol: Modbus Accessories
This product is under last time buy. Orders may be placed until 17th April 2020 and will be fulfilled based upon availability. Please contact us to discuss alternatives. |
|
Below are some cellular routers that can be used for connecting remote sites to the main office or connecting industries and offices to the internet. Also here are some of the antenna configurations for cellular IoT applications that can go along with IoT gateways.
| Compare Cellular Routers & Gateways Specs | ||
| Item | Key Specifications | Available at these Online Market Places |
|
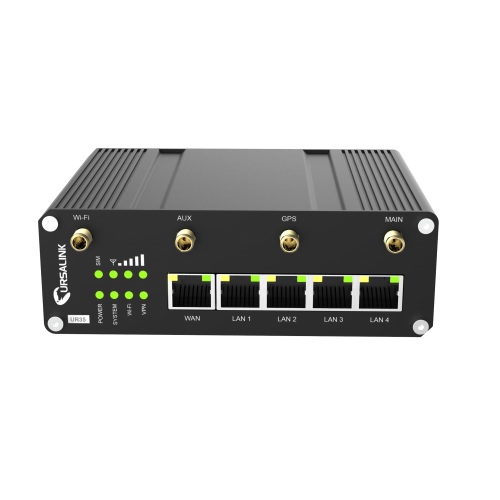
Ursalink UR35 |
Cellular Standards: 2G, 3G, LTE Cell Antenna Port: Yes Wi-Fi Standards: Wi-Fi, 802.11b, 802.11g, Wi-Fi 4 (802.11n) Wi-Fi Antenna Port: Yes |
|
|
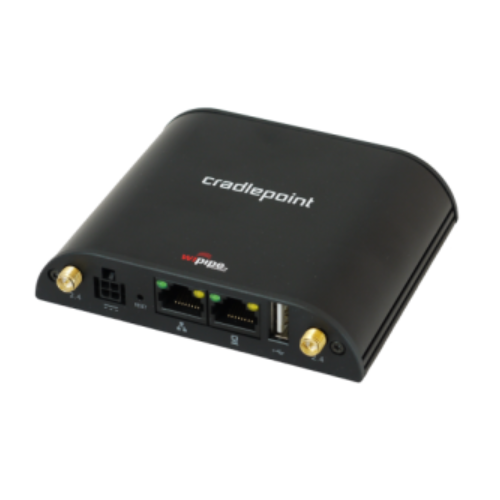
Cradlepoint E300 |
Cell Antenna Port: Yes Wi-Fi Standards: Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax), 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, Wi-Fi, Wi-Fi 4 (802.11n), Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) |
|
|
Sierra Wireless LX40 |
Cellular Standards: LTE Cell Antenna Port: Yes Wi-Fi Standards: 802.11b, 802.11g, Wi-Fi 4 (802.11n), Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) Wi-Fi Antenna Port: Yes |
|
|
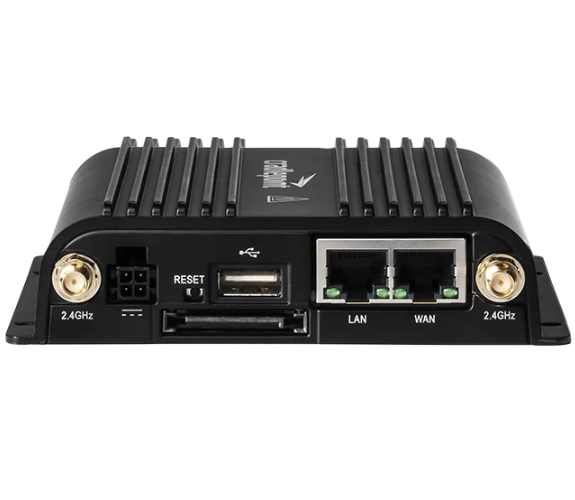
Cradlepoint IBR600C (MPN: COR IBR600C) |
Cellular Standards: LTE Cell Antenna Port: Yes Wi-Fi Standards: 802.11b, 802.11g, Wi-Fi 4 (802.11n), Wi-Fi Wi-Fi Antenna Port: Yes |
|
|
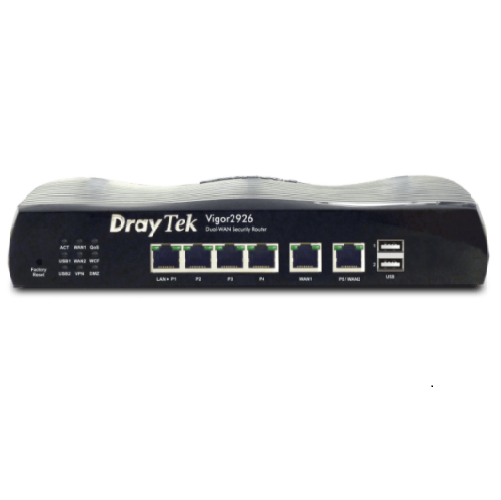
DrayTek 2926Lac |
Cellular Standards: LTE Cell Antenna Port: Yes Wi-Fi Standards: Wi-Fi 4 (802.11n), Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) Wi-Fi Antenna Port: Yes |
|
|
Peplink BPL-310X |
Cellular Standards: LTE-A Cell Antenna Port: Yes |
|
|
Cradlepoint c (MPN: COR IBR650C) |
Cellular Standards: LTE Cell Antenna Port: Yes |
|
|
Peplink BR1-SLIM-LTE |
Cellular Standards: LTE-A, LTE Cell Antenna Port: Yes Wi-Fi Standards: 802.11b, 802.11g, Wi-Fi 4 (802.11n), Wi-Fi Wi-Fi Antenna Port: Yes |
|
|
Peplink BPL-031-LTEA |
Cellular Standards: LTE-A Cell Antenna Port: Yes Wi-Fi Standards: 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, Wi-Fi 4 (802.11n), Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) Wi-Fi Antenna Port: Yes |
|
|
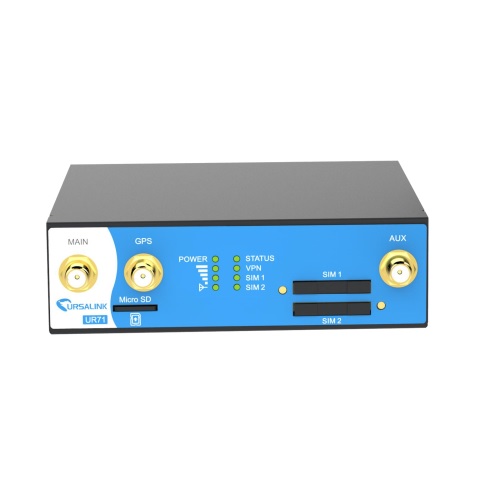
Ursalink UR71 |
Cellular Standards: 2G, 3G, LTE Cell Antenna Port: Yes |
|
|
Cradlepoint AER2200 |
Cellular Standards: LTE-A-Pro (Gigabit LTE) Cell Antenna Port: Yes Wi-Fi Standards: 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) Wi-Fi Antenna Port: Yes |
|
|
Sierra Wireless RV55-WIFI (MPN: 1104302) |
Cellular Standards: LTE-A-Pro (Gigabit LTE) Cell Antenna Port: Yes Wi-Fi Standards: 802.11b, 802.11g, Wi-Fi 4 (802.11n), Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) Wi-Fi Antenna Port: Yes |
|
|
Inseego SK160NE-ACR |
Cellular Standards: LTE Cell Antenna Port: Yes Wi-Fi Standards: Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac), Wi-Fi, 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, Wi-Fi 4 (802.11n) |
|
|
BEC Technologies MX-200A |
Cellular Standards: LTE-A Cell Antenna Port: Yes |
|
Telemetry, SCADA, Machine-to-MachineAt RFWEL Engineering we specialize in long-range BWA applications for various applications including SCADA/M2M, Video Surveillance Backhaul, Data Network Backhaul & Network Bridging Solutions. Please contact an Rfwel Engineer to discuss your application and for recommendations on the equipment required to implement your SCADA, Machine-to-Machine or remote telemetry application. Our experienced team will custom-build your solution using the best-in-class equipment and industry best-known-methods. We are also a Licensed Low-Voltage Wireless Communication contractor (Arizona ROC#322820) should you need deployment assistance. View Wireless IoT Devices supported in RFWEL's Wireless Device Information website:
|
||||
DIN Rail Mounting Bracket kit for MDS SD, iNET & entraNET AP's
|
||||
|
||||