Citizen Broadband Radio Service (CBRS) is an opened-up 150Mhz channel for spectrum sharing, that was otherwise mainly used by military ships, ground radars, and fixed satellites. CBRS operates in the 3.5 GHz spectrum (3550 – 3700 MHz) which is part of the C-band spectrum.
CBRS (Citizens Broadband Radio Service) at 3.5 GHz should not be confused with CB Radio (Citizens Band Radio) which is a two-way voice system at 27 MHz typically used by truckers.
Rfwel engineering is a certified professional installer (CPI) of CBRS systems. You can contact us to know how best to deploy CBRS fixed wireless project like:
- Campus hotspots
- Personal and small business hotspots
- Backhaul and other Fixed Wireless Access applications
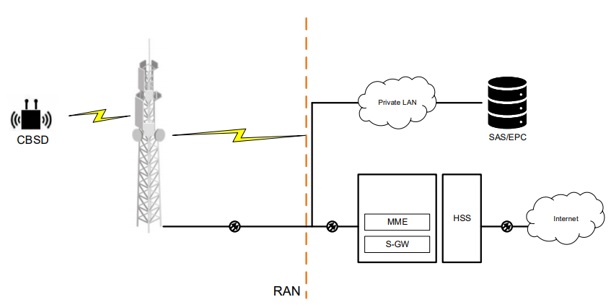
When CBRS is used for Private LTE, it is similar to traditional LTE in that it uses Evolved packet core (EPC) to access the provider’s services. This includes the mobile mobility equipment (MME), Service gateways (S-GW), and home subscriber station (HSS). The only difference comes in communication between the eNodeB (CBRSDs) and the user equipment (UE) or end-user devices (EUDs).
In LTE, each provider uses its own unique frequency bands and cannot share infrastructure. For CBRS, a common 3.5 GHz spectrum is used in a dynamic shared spectrum set up (similar in some ways to TV White Space (TVWS) or Licensed Shared Access (LSA) in Europe).
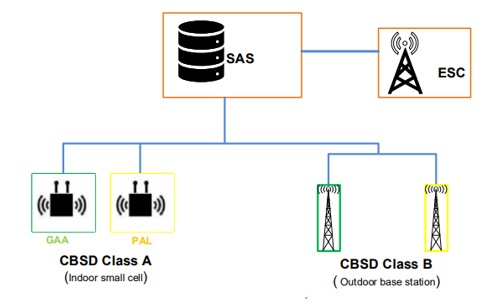
There are three tiers in the CBRS shared spectrum:
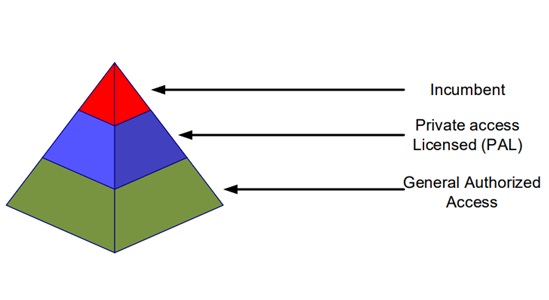
- Incumbent: They have been using this spectrum and have priority over all other tiers. They can use all the channels (10 MHz channels).
- Priority access licensed: These are licensed providers, they use 3550 -3650 MHz, and can only use 7/10 channels. They have priority over GAA.
- General authorized access: The channels are for the general public. They can use all the available channels not in use by the higher tiers. Example uses include private LTE, Campus hotspots, Personal and small business hotspots, Backhaul, and Wireless broadband services.

CBRS has the following key components.
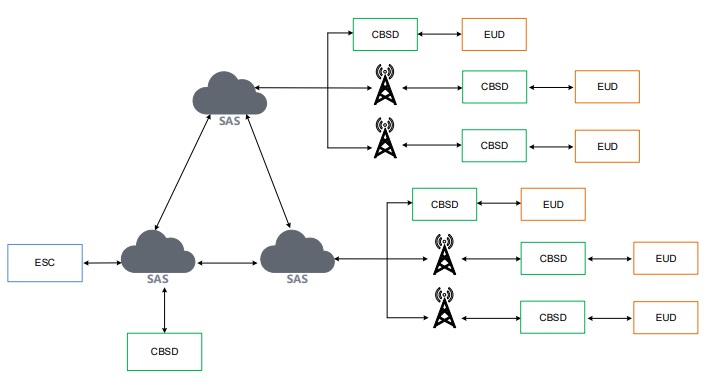
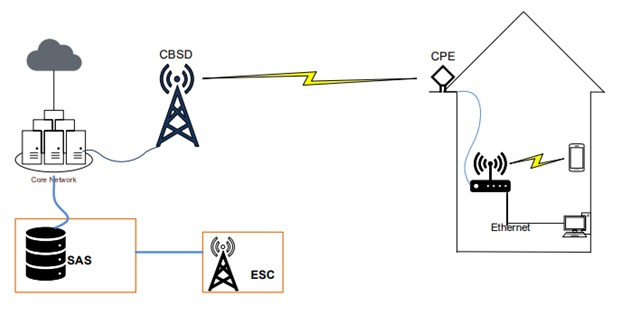
- Spectrum access System (SAS): This is the cloud service which maintains the database of the spectrum usage (like Geolocation database in TVWS). It ensures protection of higher priority users by controlling the operating parameters of lower priority users (e.g channel, transmit power).
- CBSD (CBRS Devices): These are devices operating in the CBRS frequency range (3550-3700 MHz) and communicates with SAS (e.g base station or eNodeB)
- Environmental sensing capability: Collection of sensors that detect incumbent usage and alert SAS. Mostly deployed along the coast to detect radars.
- EUD: Devices talking with CBSDs (e.g cell phone, router, outdoor CPEs). They have max EIRP of 23 dBm and can operate in the 3.5GHz range.
- DP (Domain Proxy): This aggregates communication from various CBSDs to a single SAS, sometimes for legacy radio equiment which is unaware of CBRS.
- CPI: Certified personnel who verifies the installation parameters of a CBSD and provides them to SAS.
You can view some CBRS devices and sample CBRS antennas depending on your application.
There are 2 categories of CBSD
- Category A CBSD: Has max EIRP of 30 dBm and can be used indoors or outdoors. If outdoors antenna must be less than 6 meters HAAT.
- Category B CBSD: Has max EIRP of 47 dBm and can only be used outdoors. The antenna must be less than 6 meters HAAT. Must be installed by a CBRS Certified Professional Installer (CPI) – Rfwel Engineering is a CBRS CPI (contact us to learn more).
See below sample CBRS architecture:
CBRS devices must generally follow the rules below:
- It must comply with instructions from SAS within 5mins of receipt
- If it changes location, must communicate to SAS within 60s
- Must be capable of two-way communications on the authorized frequencies.
- Can only be installed by CPI (Rfwel Engineering is a licensed CBRS CPI)
- On power-up, CBSD must report to SAS its GPS location, Elevation, its category, and FCC ID, PAL, or GAA
CBRS for private LTE is based on TD-LTE with one difference being different spectrum emissions mask requirements. The CBRS band is LTE Band 48. The UL/DL TDD configuration needs to be localized because of possibly non-planned deployments.
Considering the Right Cable for your CBRS Deployment
Signal attenuation, or the loss of signal strength in coax or networking cables, is typically measured in a logarithmic scale, i.e., decibels (dB). Cable attenuation or loss is directly proportional to the frequency and the length (i.e., the longer the cable the higher the loss or the higher the frequency the higher the loss).
CBRS radios operate in the 3.55 to 3.7 GHz band (3550 – 3700 MHz) thereby posing a greater signal loss challenge than other LTE/NR radios that operate at lower frequency bands. It is therefore important to choose the right low-loss cable when the cable run is longer than say about 100ft.
A suitable option for long cable runs is the 600 series cable which has a lower attenuation compared to the 400-series making them suitable for longer runs. This way you can achieve the desired EIRP without having expensive and bulky high gain antennas.

For example, at 3.7 GHz which is the upper end of the CBRS band, a 600-series will attenuate the signal by only about 6.2 dB/100 ft. See the comparison below with 400-series and 240-series cables of various lengths.
|
3700 MHz Application (upper end of CBRS and part of C-Band Block A) |
|||
|
Cable Length |
100 ft |
200 ft |
300 ft |
|
6.2 dB |
12.3 dB |
18.5 dB |
|
|
9.4 dB |
18.6 dB |
27.8 dB |
|
|
17.7 dB |
35.2 dB |
52.7 dB |
|
Consider these 300ft, 250ft, 200ft, 150ft, and 100ft 600-Series cable lengths available on amazon.
Rfwel can custom build your custom cable with appropriate connectors and pigtails to interface your radio equipment and antennas. We also offer cables suitable for different environments, e.g., outdoor UV protected, plenum-rated cables, flexible cables for tight spaces, etc.
Migrating from Legacy Wireless Broadband Service (e.g., WiMax) Solutions to CBRS
The 3650 –3700 MHz service was created in 2005 when FCC opened this spectrum for Wireless Broadband services (WBS). However, with the introduction of the CBRS spectrum, the WBS devices need to shift to use the CBRS SAS (Spectrum Access System).
WiMax radios were using the 50 MHz WBS band, i.e., 3.65-3.7 GHz (3650-3700 MHz) (other WiMax radios, e.g., Clearwire which was later acquired by Sprint, used the 2.5 GHz band (LTE Band 41).
After the FCC approved CBRS SAS in 2015, radios operating in the WBS band were treated as incumbents and were grandfathered/protected from interference until April 17, 2020. WBS providers now have to shift and operate on a GAA (General Authorized Access) basis as other lowest tier CBRS devices.
Unlike WiMax which was lightly licensed in the WBS band, GAA users in the CBRS band of the SAS system are unlicensed and this provides opportunities for operators, and businesses to increase their wireless coverage with CBRS devices.
The comparison below shows a typical WiMAX set up for Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) and an equivalent CBRS setup for much faster and more flexible FWA.

With CBRS, the technology can achieve more than 100Mbs depending on the distance from base stations. An added advantage of the spectrum sharing (SAS) system is that at GAA device can utilize additional frequencies up to around 150 MHz if PAL devices and incumbents are not utilizing those frequency bands.
CBRS Defining Bodies
|
United States Federal Communications Commission FCC
|
Wireless Innovation Forum WinnForum
|
CBRS Alliance
|
Incumbents
|
Incumbent Users |
|||
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Military Ship-borne Radar |
Military Ground-based radar |
Fixed Satellite service earth stations (Receive only) |
Wireless Broadband Services |
|
3550-3650 MHz |
3550-3700 MHz |
3600-3700 MHz |
3650-3700 MHz |
|
Operates in the coastal areas They may have significant activities in specific areas like San Diego. |
Occasional Operations at various military bases around the country |
Few number of sites in the country operating in receive mode in the CBRS band. |
Various sites operating around the country. They are transitioned to operate as CBRS users (GAA or PAL) |
Contact an Rfwel CBRS Certified Professional Installer (CPI) to learn more about how you can migrate your legacy WBS system to CBRS or how you can use CBRS on your next greenfield Fixed-Wireless Access (FWA) project. You may also reach us at +1.480.218.1877 Option 2.